ASOURCE®NAVI

公開日:2022.01.18
新型コロナウイルスの新変異株とされる「オミクロン株」が本邦で見つかってから1ヶ月余りが経過しました。国内のオミクロン株の感染者は空港検疫も含め累計1,000人を超え、多くの都道府県で確認されています。オミクロン株の感染性や重症度など現時点の研究でわかっている情報をまとめました。
デルタ株が世界で収束しないなかで、オミクロン株は2021年11月24日に南アフリカから報告され、世界保健機関(WHO)が「懸念される変異株」に指定しました。その後、欧州へ拡大し世界的に感染が広がり、12月29日時点で128の国で確認されています。
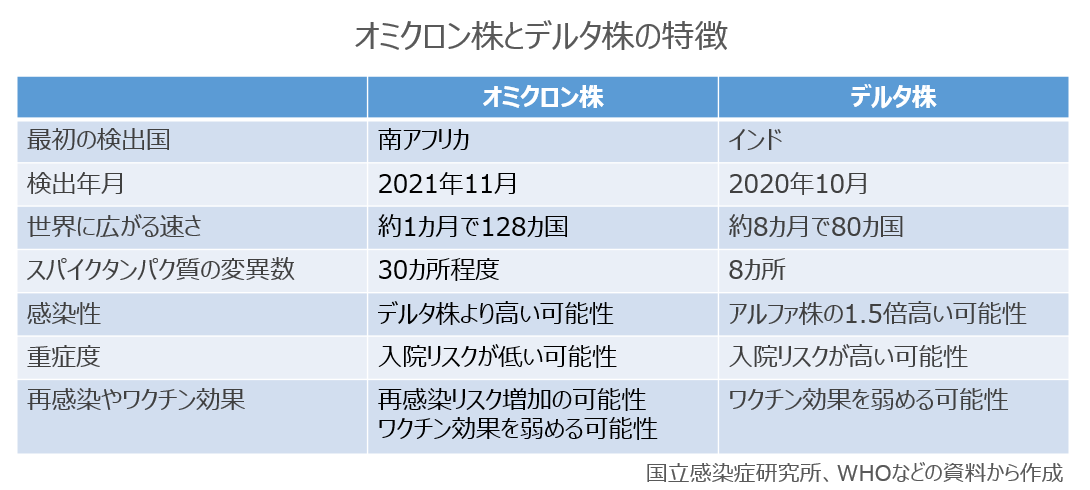
本邦で初めてオミクロン株が確認されたのは、昨年11月28日に入国した人のケースでした。その3週間後には市中感染が確認され、急速に全国に拡大しつつあります。専門家は、近いうちにデルタ株からオミクロン株への置き換わりが起こる可能性が高い、と指摘しています。感染力の強さは著しく、感染者1人が他者にうつす平均人数「実効再生産数」はデルタ株の3〜6倍とされます。
オミクロン株はウイルス表面にあるスパイクタンパク質の遺伝子に30か所程度の遺伝子変異があり、このうち15か所程度の変異が感染の成立に関わる受容体結合部位に存在しています。これによって、従来のコロナウイルスよりもヒトの細胞に結合しやすくなった可能性が考えられます。
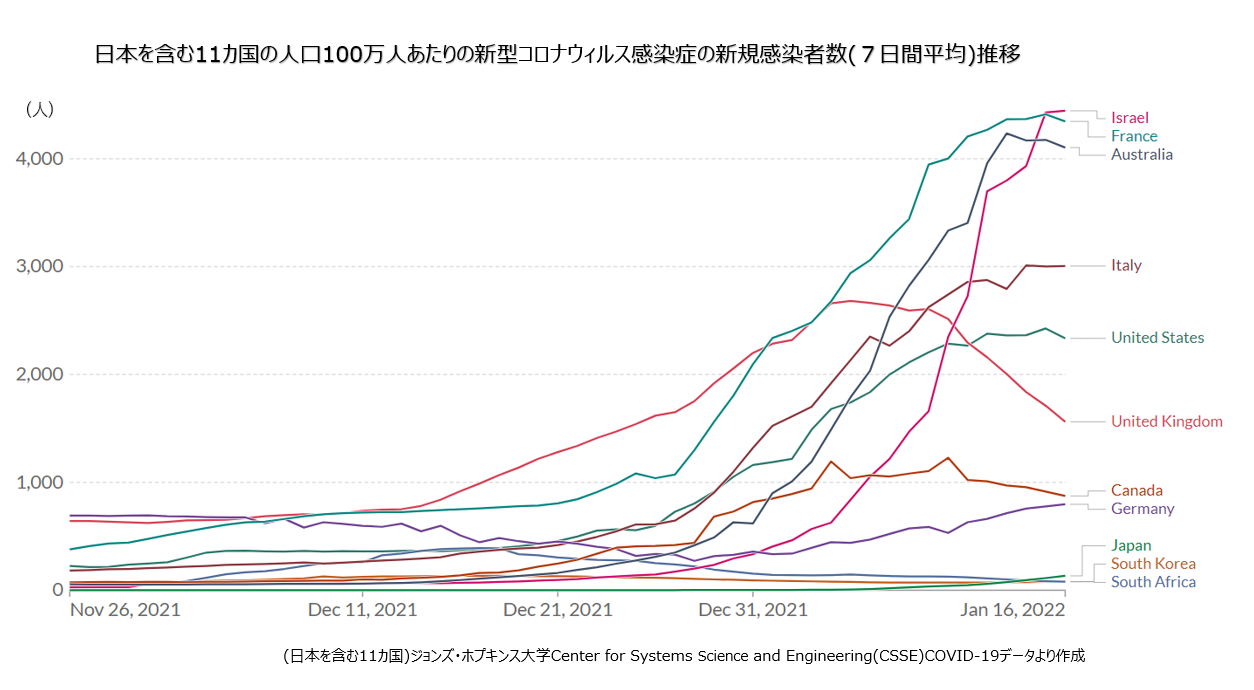
オミクロン株の倍加時間(累積の感染者数が2倍になるまでにかかる期間)は、英国や南アフリカなどの流行地の分析結果より、およそ2〜3日間と短いことが報告されています。オーストラリアでは、オミクロン株の市中感染が初めて確認された昨年12月3日以降に感染が急拡大し、当時1,500人程度だった新規感染者数が今年1月8日には約8万8,000人と過去最多となりました。オミクロン株が主流となりつつある英国、米国、フランスなどでは、1日あたりの新規感染者数が過去最多を更新し、ブレイクスルー感染も相次いで報告されています。
ロンドンでの調査によると、オミクロン株感染者で多かった症状は鼻水、頭痛、疲労、咽頭痛など一般的な風邪と同じだったといいます。WHOも肺炎を引き起こす他の変異ウイルスと異なり、鼻や喉など上気道の炎症にとどまるケースが多いとの見解を示しています。
オミクロン株は従来の変異株よりも重症化しにくいとする研究結果がいくつか報告されています。英・インペリアル・カレッジ・ロンドン(ICL)の研究によると、オミクロン株の感染者はデルタ株の感染者と比べて、一泊以上入院するリスクは40〜45%低いと推計されています。英保健安全保障庁(UKHSA)もオミクロン株感染による入院リスクはデルタ株の約3分の1程度であることを公表しています。また、南アフリカ国立伝染病研究所の研究でも、入院リスクは他の変異株よりも70%低いというものでした。
本邦の研究グループ「G2P-Japan」はオミクロン株の病原性は弱い可能性があるとする動物実験の研究結果を明らかにしました。病原性の評価には、体重の変化が1つの指標となります。ハムスターに従来株、デルタ株、オミクロン株をそれぞれ感染させて体重の変化を調べると、非感染群の5日目の体重は10%増加しましたが、感染5日目の従来株群とデルタ株群の体重はそれぞれ10%以上減少しました。これに対して、オミクロン株群の体重はほぼ不変でした。呼吸機能については、従来株群、デルタ株群とも酸素飽和度は感染2日目より急激に低下しましたが、オミクロン株群はわずかな低下で非感染群とほとんど変わリませんでした。また、日米の研究者グループの報告では、オミクロン株に感染させたハムスターでは、他の変異株よりも肺の損傷が著しく少ないことがわかりました。これらの結果から、オミクロン株の病原性は弱い可能性が考えられます。
オミクロン株に対するワクチンの効果については、ワクチンが接種後にスパイクタンパク質に対する抗体ができるように設計されているため、スパイクタンパク質に多くの変異があるオミクロン株に対しては、効果が低下するとみられています。UKHSAの報告によると、オミクロン株に対するファイザー製もしくはモデルナ製の発症予防効果はデルタ株に比べて低く、2回目の投与後65〜70%程度であった効果は、20週目には10%程度に減少していました。ブースター接種後2〜4週間のワクチン効果は約65〜75%で、5〜9週間では55〜65%、10週間以上では45〜50%に低下していました。
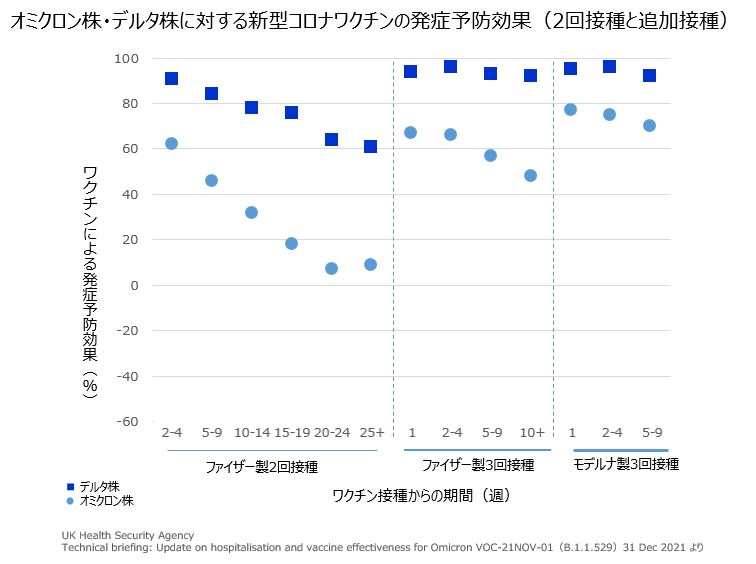
また、ICLの研究から、過去の感染によって免疫を持つ人でもオミクロン株により再感染しやすくなり、オミクロン株による再感染リスクはデルタ株に比べて5倍以上高いとされます 。
オミクロン株の登場は治療薬にも影響を及ぼしています。昨夏に特例承認された抗体医薬ロナプリーブはオミクロン株に対して中和活性が低下することが実験でわかり、厚生労働省は昨年12月に、オミクロン株の感染例の場合には同薬剤は推奨されないとする通知を出しました。
これまでの研究からオミクロン株の特徴として、①感染力が強い②症状が軽い③重症化率が低い④再感染リスクが増加する⑤ワクチンの効果を弱めるなどが挙げられます。現時点でオミクロン株の重症化の頻度は少ないとみられますが、感染者が爆発的に増えると一定の割合で入院患者、重症者が出てくるため、医療の逼迫を引き起こす可能性が高まります。また、高齢者など重症化リスクのある人たちに感染が広がれば、大きな影響が出る恐れもあります。ワクチンの追加接種も含め感染対策の徹底が望まれるところです。
メディアスグループは、医療機器の販売を中心とした事業を展開しています。医療に携わる私たち(Medical+us)は、医療現場や人々の健康的な明日へ役立つ情報をお届けする情報発信源(Media)の役割も果たしていきたいと考えています。