ASOURCE®NAVI

公開日:2023.01.06
前回の医薬品の薬事承認の仕組みに続き、今回は医療機器の薬事承認の仕組みについて、最近の動向も踏まえご紹介します。
医療機器を市場に流通させるためには、薬機法(医薬品、医療機器等の品質、有効性及び安全性の確保等に関する法律)に定められた医療機器のクラス分類と、分類による医療機器の審査、認証、承認手続きが必要となります。医療機器の承認や認証は、製造販売される医療機器が、品質や有効性・安全性等の観点から、医療機器として問題がないかどうかを審査して与えられます。
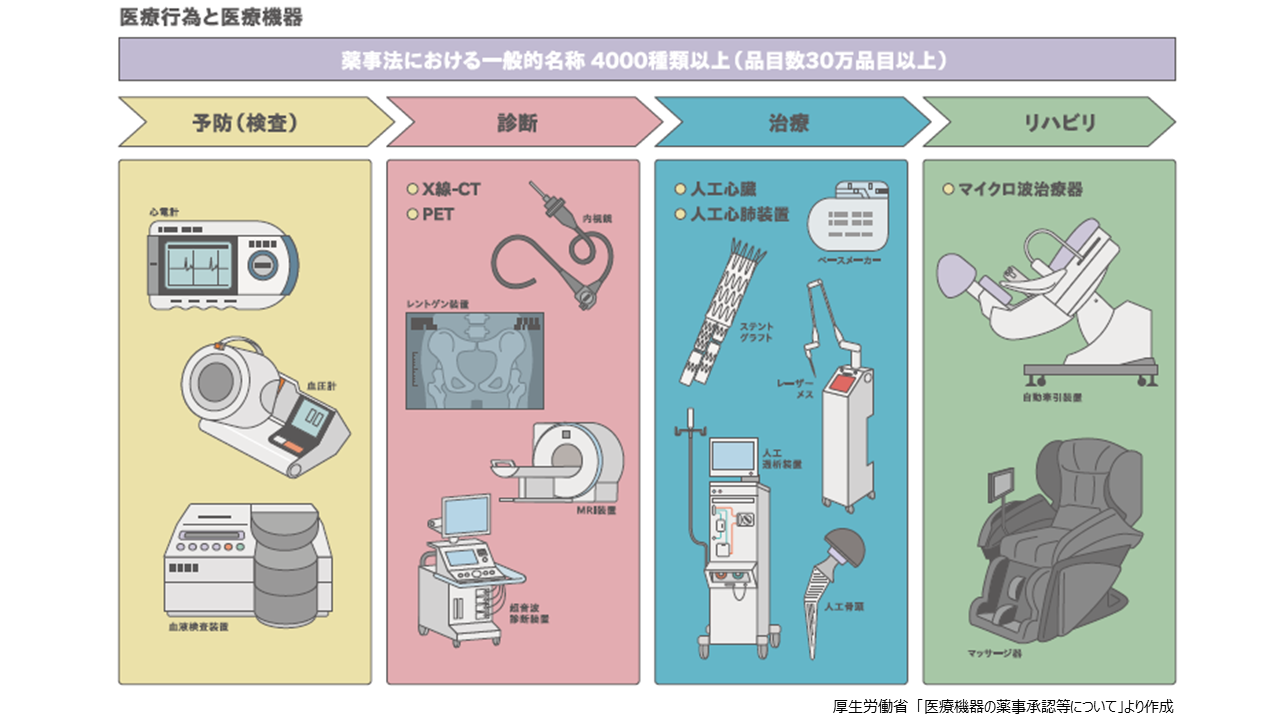
医療機器を用途で分けると、①予防(検査)②診断③治療④リハビリの4つに大別されます。①予防(検査)機器としては、心電計、血圧計、血液検査装置など。②診断機器としては、内視鏡、レントゲン装置、超音波診断装置、X線-CT、MRI、PETなど。③治療機器としては、レーザーメス、ペースメーカー、人工心臓、ステントグラフト、人工透析装置、人工心肺装置、人工骨頭など。④リハビリ機器としては、自動牽引装置、マイクロ波治療器、マッサージ器などがこれに該当します。これらの医療機器は薬機法の対象となりますが、医療現場で使われているサージカルマスクやプラスチック手袋などは雑貨(雑品)扱いで、薬機法規制の対象外となります。
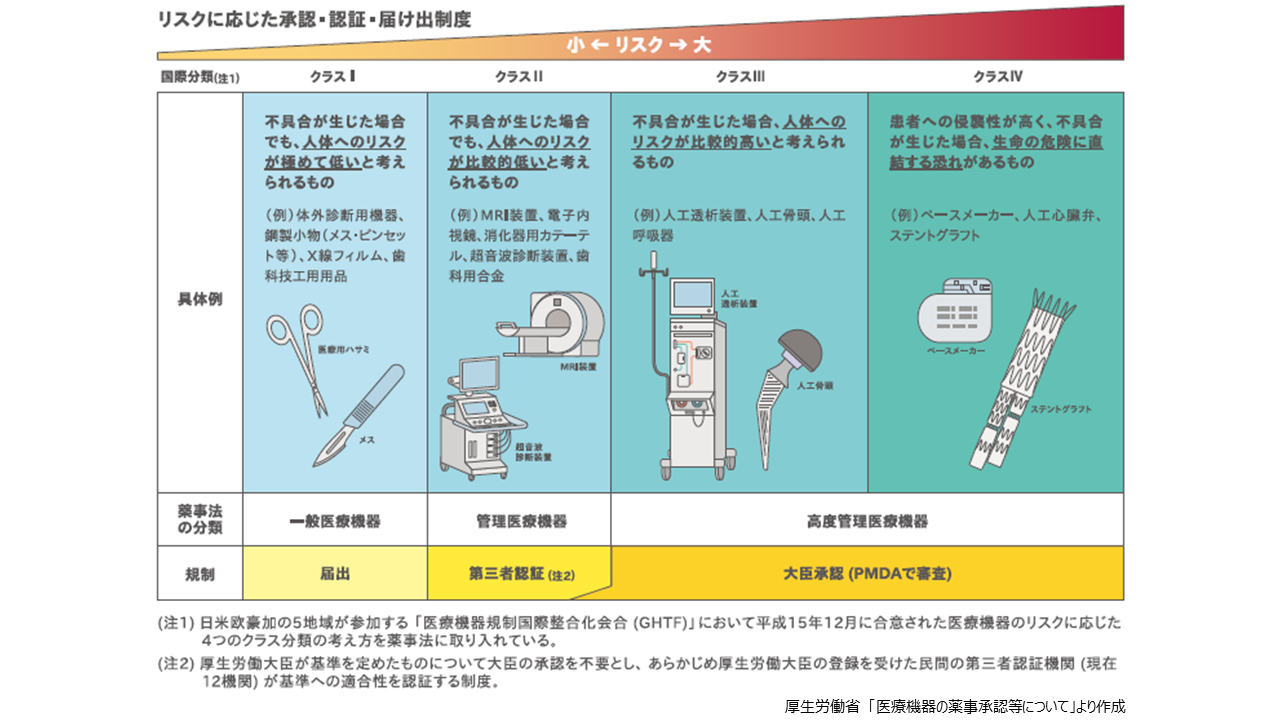
薬機法によるクラスは医療機器の人体へのリスクの大小によって分類されています。必要となる手続きは、該当するクラスで異なります。一般医療機器(国際分類:クラスI)は、不具合が生じた場合でも、人体へのリスクが極めて低いものと考えられるもので、体外診断用機器、鋼製小物(メス・ピンセットなど)、医療ガーゼ、脱脂綿、X線増感紙、歯科用印象材料などが挙げられます。これらの機器は、医薬品医療機器総合機構(PMDA)に届出を行った時点で製造販売が開始できます。管理医療機器(同:クラスII)は、不具合が生じた場合でも、人体へのリスクが比較的低いと考えられるもので、MRI装置ワークステーション、眼科用内視鏡、気管支カテーテル、超音波血流計、歯科用金属などが挙げられます。これらの機器については、製造販売に際して厚生労働大臣の登録を受けた民間の第三者認証機関に認証申請を行い、認証を得る必要があります。
高度管理医療機器はクラスIIIとクラスIVに分けられ、クラスIIIは不具合が生じた場合、人体へのリスクが比較的高いと考えられるもので、中空糸型透析器、人工関節、麻酔用人工呼吸器、眼科用マイクロカテーテルなどが挙げられます。また、クラスIVは、患者への侵襲性が高く、不具合が生じた場合、生命の危機に直結する恐れがあるもので、植込み型心臓ペースメーカー、冠動脈用ステント、大動脈用ステントグラフトなどが挙げられます。これらの機器については、PMDAに承認申請が必要となります。PMDAで医療機器の品質、有効性、安全性について審査を行い、薬事・食品衛生審議会に諮問・答申を経て厚生労働省が薬事承認します。
また、PMDAでは申請区分として①新医療機器(既に製造販売承認を与えられている医療機器と構造、使用方法、効果、性能が明らかに異なる)②改良医療機器(新医療機器または後発医療機器のいずれにも該当しない)③後発医療機器(既承認医療機器と構造、使用方法、効果、性能が実質的に同等である)と分類しています。
審査に必要な添付資料としては、仕様の設定、安定性、効能、リスク分析、製造方法、臨床試験成績などに関するものです(申請する医療機器によって必要な資料や試験が変わりますので、医療機器によっては不要な資料もあります)。
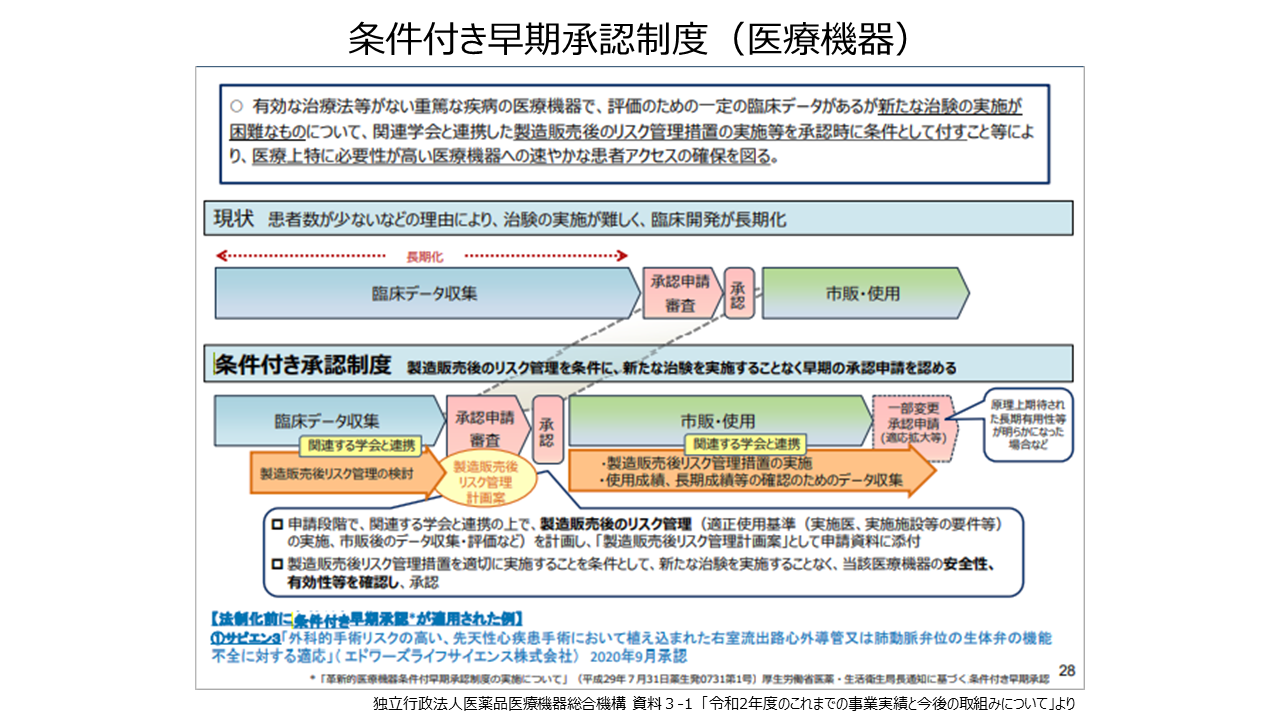
有効な治療法がない重篤な疾病の医療機器で、一定の臨床データがあるものの、患者数が少ないなどの理由により新たな治験の実施が困難なものについて、関連学会と連携した製造販売後のリスク管理措置の実施などを承認時に条件として付すことなどにより速やかな患者アクセスの確保を図る「条件付き早期承認制度」があります。これまで肺動脈弁位に植込まれた弁付き導管・外科用生体弁の再治療を目的としたTPVI(経カテーテル肺動脈弁治療)用のバルーン拡張型人工心臓弁「エドワーズ サピエン3」などが適用されています。また、最近はAIを使って開発された医療機器(内視鏡画像診断支援ソフトウエア)や行動変容アプリ(禁煙治療補助システム)なども開発され、それらの審査の迅速化や透明性が進められています。
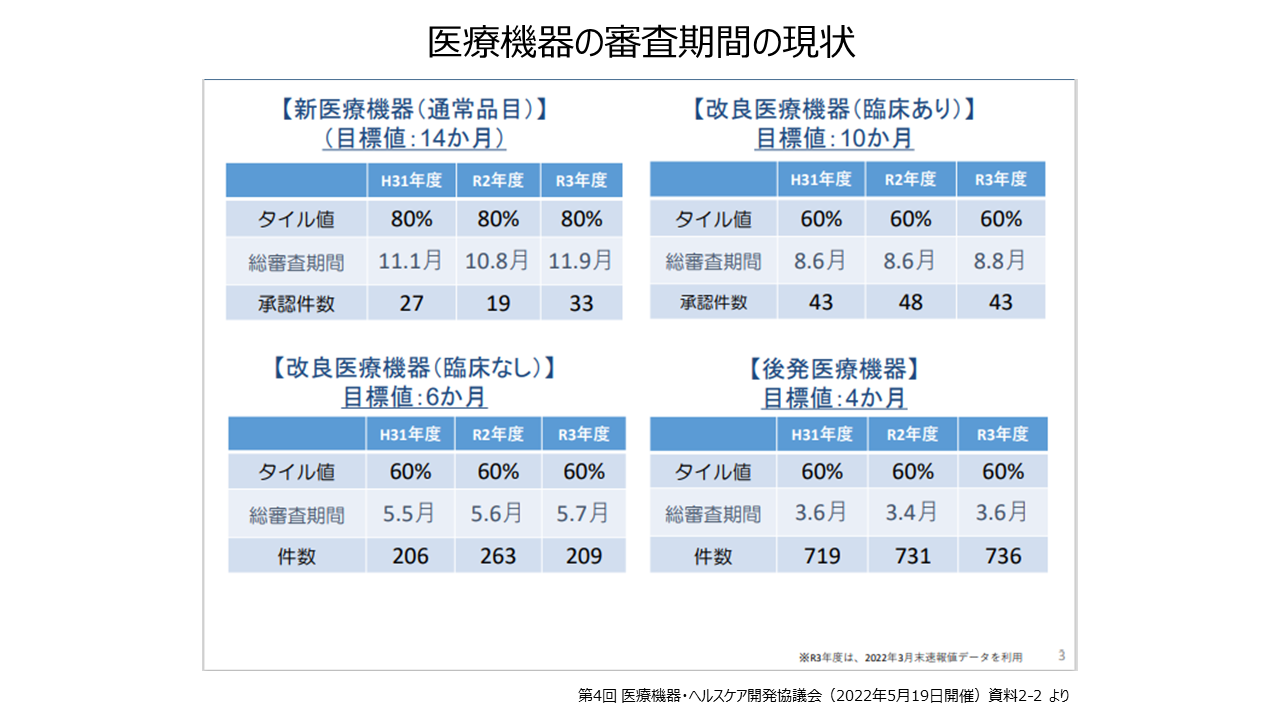
医療機器の年間の承認件数は2021年では、新医療機器(通常品目)が33件、改良医療機器(臨床あり)が43件、改良医療機器(臨床なし)が209件、後発医療機器が736件となっています。
審査期間は、新医療機器が11.9月(80%タイル値)、後発医療機器が3.6月(60%タイル値)などとなっています。行動変容を伴うプログラム医療機器の承認件数は、平成27年は9件であったのが、令和1年には36件と増加しています。
医療機器の実用化までの期間の短縮はそれを待つ患者のメリットになるうえ、企業にとっても事業を進めるうえで好材料といえます。
メディアスグループは、医療機器の販売を中心とした事業を展開しています。医療に携わる私たち(Medical+us)は、医療現場や人々の健康的な明日へ役立つ情報をお届けする情報発信源(Media)の役割も果たしていきたいと考えています。