ASOURCE®NAVI

公開日:2024.01.15
臓器移植は、臓器の機能が低下し、他の方法では治療できない状態にある患者に対して、他の人から提供された臓器を移植する医療プロセスです。これは、善意による臓器提供者(ドナー)と社会全体の理解と支援によって成り立っています。臓器移植の仕組みを2回にわたってまとめます。第1回目は臓器移植のルール、主な流れ、ドナー登録について紹介します。
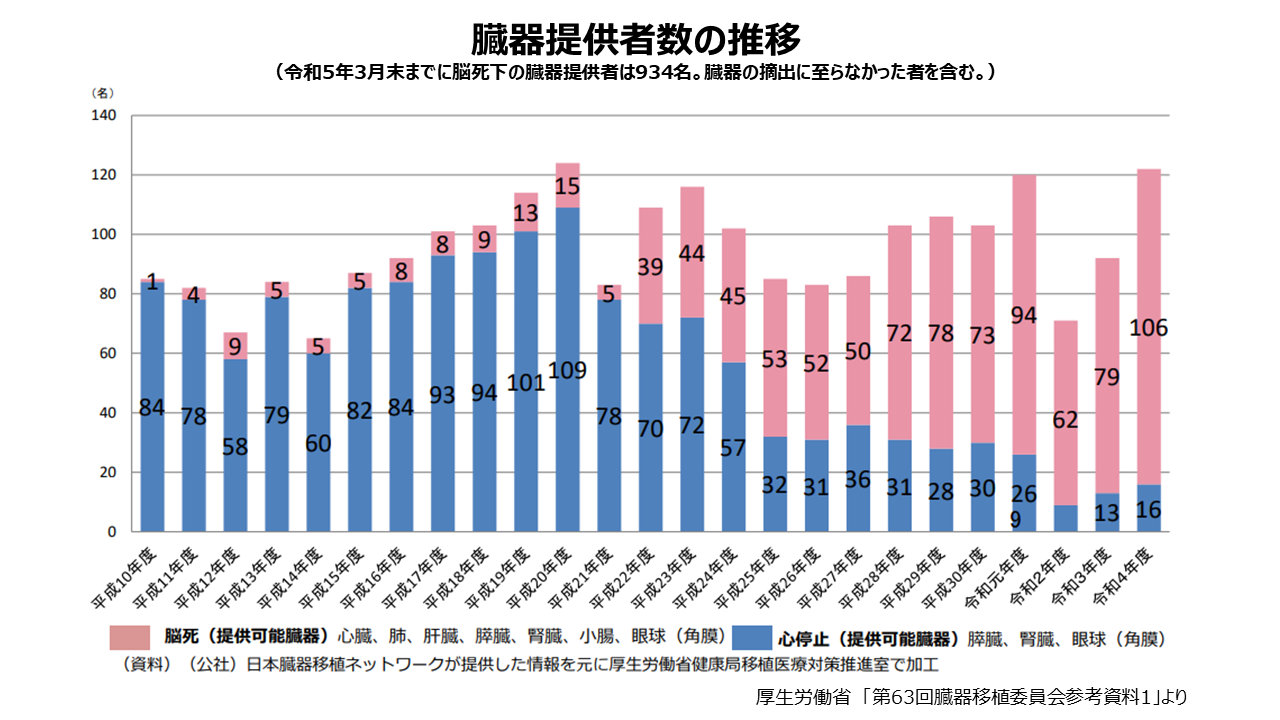
日本では、臓器移植法施行前は心停止後に腎臓と角膜移植のみが可能でしたが、1997年10月に臓器移植法が施行され、事前の本人の意思表明に基づいて、脳死と判定された人から心臓や肺、肝臓などの臓器が提供できるようになりました。そして、臓器移植法の改正に伴い2010年7月からは、本人の意思が確認できなくても家族の同意があれば臓器提供できるように変わりました。これによって、15歳未満であっても脳死下の臓器提供が可能となり、小さな身体の子どもたちの心臓や肺の移植の道が開かれました。以降、脳死と判定された人からの臓器提供は増え、心停止後の臓器提供は減少傾向にあります。提供可能な臓器は、臓器移植法や施行規則によって定められ、脳死下は心臓、 肺、肝臓、腎臓、膵臓、小腸、眼球、心停止後は腎臓、膵臓、眼球となっています。これとは別に家族などからの生体移植も行われています。脳死下での移植は、直前まで臓器への血流があるため、心停止後よりも移植できる臓器の種類が多くなります。
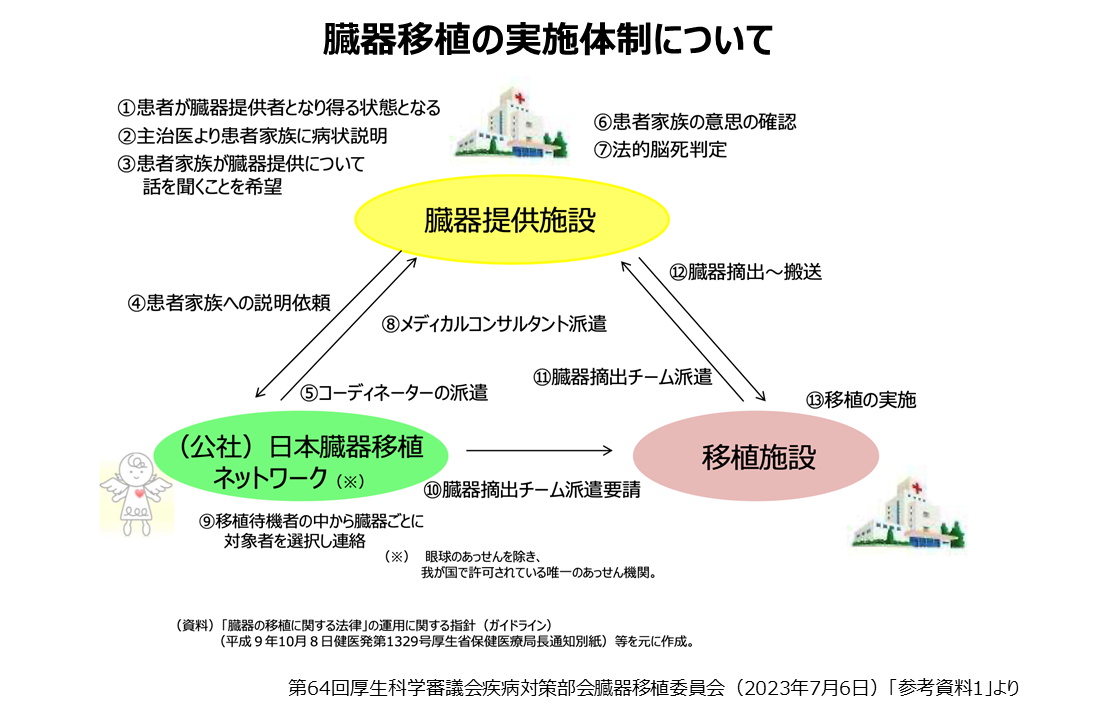
臓器提供の主な流れは次の通りです。
1.ドナーの選定:
ドナーの対象となるのは、事故や病気などで救命救急センターに搬送され、最善の治療を受けても助かる見込みがなく、主治医が「脳死とされうる状態」と診断した場合です。
2.臓器提供についての説明と家族の意思決定:
主治医らは家族に病状説明とともに臓器提供に関する情報を提供します。家族から「臓器移植について話を聞きたい」という申し出があると、主治医らは臓器移植コーディネーターに連絡し、コーディネーターが派遣されます。家族はコーディネーターから詳細な情報を受けることになります。家族は十分に話し合い、臓器提供の意思決定をします。提供しないと判断した場合にも不利益な扱いを受けることはありません。
3.脳死判定:
家族が臓器提供を決めると、法律に基づいた脳死判定が2回行われます。1回目と2回目の脳死判定は、それぞれ6時間以上(6歳未満の場合は24時間以上)の間を空けて行われます。脳死判定には、移植とは無関係な経験と知識のある医師2人が関与します。家族が立ち合うことも可能です。2回目の脳死判定が終わった時間が死亡時刻となります。
4.移植候補者の選定:
日本臓器移植ネットワークに登録の移植希望者の中から、条件に合致した移植候補者がコンピューターによって公平に選ばれます。
5.臓器摘出と移植:
臓器提供が承諾されると、すみやかに臓器摘出手術が行われます。提供された臓器は移植者のもとに運ばれて移植手術が行われます。臓器提供を行う医療機関は大学病院や日本救急医学会の指導医指定病院、救命救急センター認定施設などの「5類型施設」で895施設に限られていますが、このうち、18歳未満を含め体制が整っている施設は284施設、18歳以上の体制が整っている施設は153施設とされます(2023年3月末時点)。移植が可能な施設は、心臓11施設、肺11施設、肝臓23施設、膵臓21施設、腎臓125施設、小腸13施設となっています(同)。
6.身体のお戻し:
摘出手術後、提供者のお身体はきれいに縫合され、家族の元に戻ります。 その後は通夜や葬儀など、ご家族や大切な方々との時間をお過ごしいただけます。
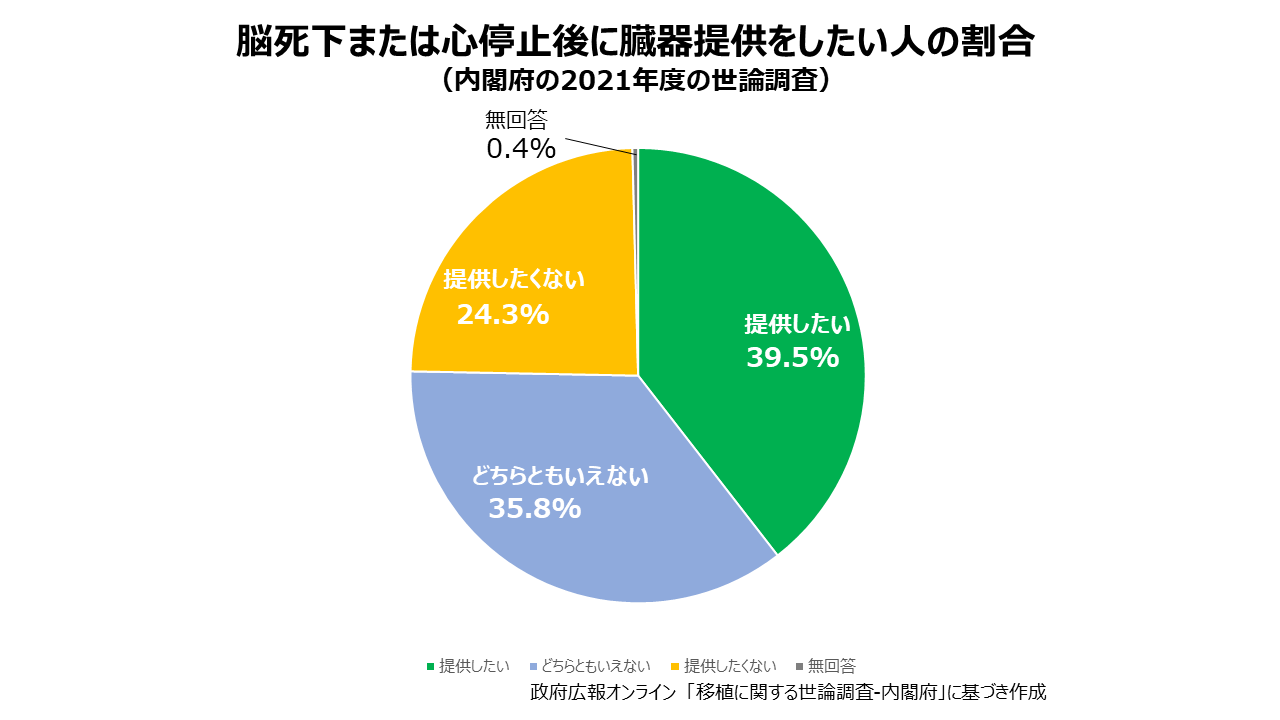
臓器提供をするには、本人もしくは家族の同意が必要です。臓器提供の意思表示は、運転免許証や健康保険証、マイナンバーカード、意思表示カードにその旨(同意するかしないか)を記すことで意思表示をすることができます。インターネットによる臓器提供意思登録サイトでの登録も可能です。意思表示をした場合、その意思を家族に伝えておくことが大切です。2016年に日本臓器移植ネットワークが実施した意識調査では、臓器提供を「したい」「したくない」にかかわらず、意思表示カードや運転免許証、健康保険証での意思表示率は、全体の 10.3%〜11.2%でした。また、内閣府の2021年度の世論調査では「脳死下または心停止後に臓器提供したい」と回答した人の割合は 39.5%であったものの、実際に「臓器提供に係る意思表示を行っている」と回答した人の割合は 10.2%とギャップがみられており、臓器提供をしたいと思っていても、多くのケースにおいて、必ずしも具体的な「意思表示」という行動に結びついていない現状が浮かび上がっています。
次回は、「臓器提供の仕組み2」として、臓器移植希望者、海外の状況、今後の課題について紹介します。
メディアスグループは、医療機器の販売を中心とした事業を展開しています。医療に携わる私たち(Medical+us)は、医療現場や人々の健康的な明日へ役立つ情報をお届けする情報発信源(Media)の役割も果たしていきたいと考えています。