Release date: 2025.06.02
In recent years, advances in medical technology have led to rapid developments in minimally invasive treatments, making them a less burdensome option for many patients. While traditional open surgery inevitably leaves large wounds, minimally invasive treatments require minimal incisions and shorten recovery times, thereby contributing to improving patients' quality of life (QOL). This article will explain minimally invasive treatments in two parts. In the first part, we will provide a detailed explanation of the definition and history of minimally invasive treatments, the diseases they target, and the main treatment methods, and consider their evolution and future prospects.
Minimally invasive treatment is a general term for medical techniques that treat illnesses while reducing the burden on the patient. It refers to methods that require smaller incisions than traditional surgical procedures, or treatments that do not involve incisions at all. The reason it is called "minimally invasive" is because it reduces the size of the wound and allows treatment to be performed while minimizing pain and bleeding. In other words, it means that there is minimal invasion into the patient's body.
The introduction of this treatment method offers many benefits, such as shorter hospital stays, faster postoperative recovery, and reduced risk of infection. As a result, it is expected that patients will be able to return to society sooner and that the psychological and physical burden will be reduced.
Although the concept of minimally invasive treatment is relatively new, various technological innovations have been made over the years. In the 1970s, advances in endoscopic technology made it possible to examine the digestive system, improving diagnostic accuracy and enabling more appropriate treatment options. In the 1980s, laparoscopic surgery became widespread, and minimally invasive surgeries such as cholecystectomy became commonplace. Furthermore, in the 2000s, robotic-assisted surgery emerged, enabling more precise surgery. Currently, advances in catheter therapy and navigation technology are expanding the scope of application of minimally invasive treatment. These technological innovations have made it possible to improve the quality of treatment while reducing the burden on patients.
Minimally invasive treatments offer significant benefits when applied to specific diseases.
<Neurosurgical diseases>
Advances in endoscopic technology have enabled high-resolution visual fields and the development of specialized instruments, making it possible to operate on brain tumors (such as pituitary adenomas) through small incisions.
<cancer>
Contributing to early cancer treatment by utilizing endoscopic surgery and radiation therapy
Heart disease
Catheter surgery allows repair of blood vessels and valvular disease while avoiding conventional open-heart surgery
<Orthopedic diseases>
Arthroscopic surgery allows for safer treatment of arthritis and ligament injuries
<Gynecologic diseases>
Laparoscopic procedures such as uterine myomectomy reduce the burden on patients
Minimally invasive treatments for these diseases offer the potential for faster recovery and reduced risk of complications compared to conventional treatments.
Minimally invasive treatments are mainly categorized into the following methods:
Endoscopic surgery: This type of surgery is performed using an endoscope such as a laparoscope or thoracoscope to insert long, thin instruments through small holes. Specialized instruments are operated through multiple small incisions while observing the surgical field with a high-resolution camera. Compared to regular open abdominal or thoracotomy, this type of surgery is characterized by a faster recovery time and less pain at the incision.
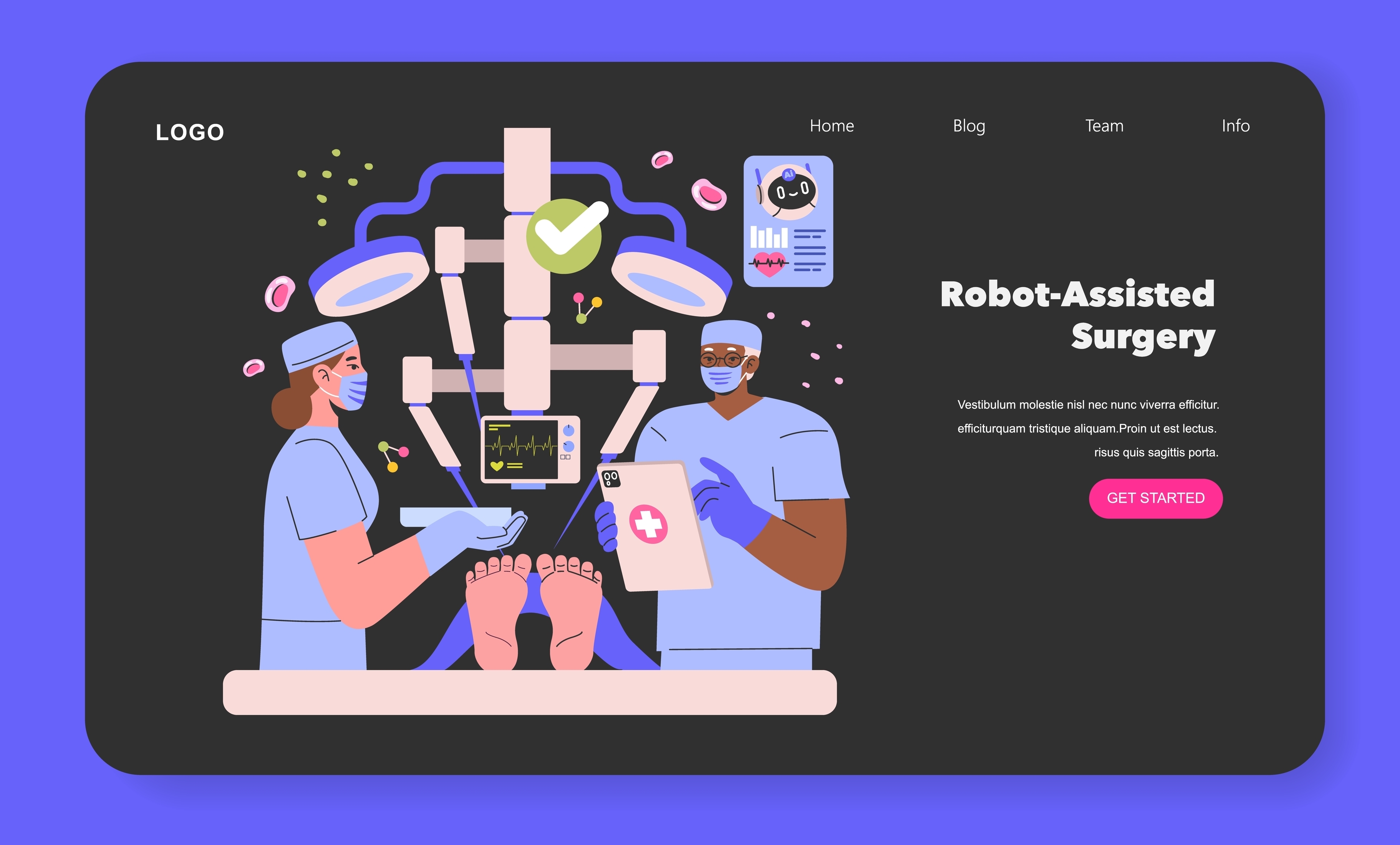
Robotic surgery: This type of surgery uses a robotic arm remotely controlled by a surgeon. Robotic arms, capable of high-resolution 3D vision and precise movements, enable more delicate and complex surgeries. They are particularly popular for radical prostatectomies and colon cancer surgeries.
Catheter therapy: Also known as endovascular therapy, this is a treatment performed by inserting a thin tube (catheter) into the blood vessels. Examples include percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and cerebral aneurysm coil embolization. Compared to surgery, this treatment places a much smaller physical burden on the body and can often be applied to elderly patients and those in poor general health.
Each of these treatments has its own characteristics and indications, and they enable treatments that were previously difficult to perform. Furthermore, these technologies continue to evolve rapidly, and are expected to become even less invasive and more accurate. These treatments are adapted to each disease and patient's condition, enabling safer and more effective treatments.
Minimally invasive treatments have developed alongside advances in medical technology, and have been established as new treatment options that reduce the burden on patients. Further technological innovations will likely continue, making it possible to treat an even greater number of diseases. We look forward to a future in which safer and more comfortable treatments are available for patients.
MEDIUS Group is developing a business centered on the sale of medical equipment. We (Medical + us) involved in medical care also want to play the role of an information source (Media) that delivers useful information for the medical field and people's healthy tomorrow.